Solar panel virtual net metering is revolutionizing the way communities and individuals harness solar energy. As the world increasingly looks for sustainable energy solutions, virtual net metering offers an innovative approach that not only benefits individual consumers but also contributes to larger environmental goals.
Introduction to Solar Panel Virtual Net Metering
In recent years, the adoption of solar energy has surged, driven by advancements in technology, declining costs, and growing environmental awareness. One significant development in this field is the concept of virtual net metering, which enables multiple energy consumers to share the benefits of a single solar energy system.
Understanding Virtual Net Metering
What is Net Metering?
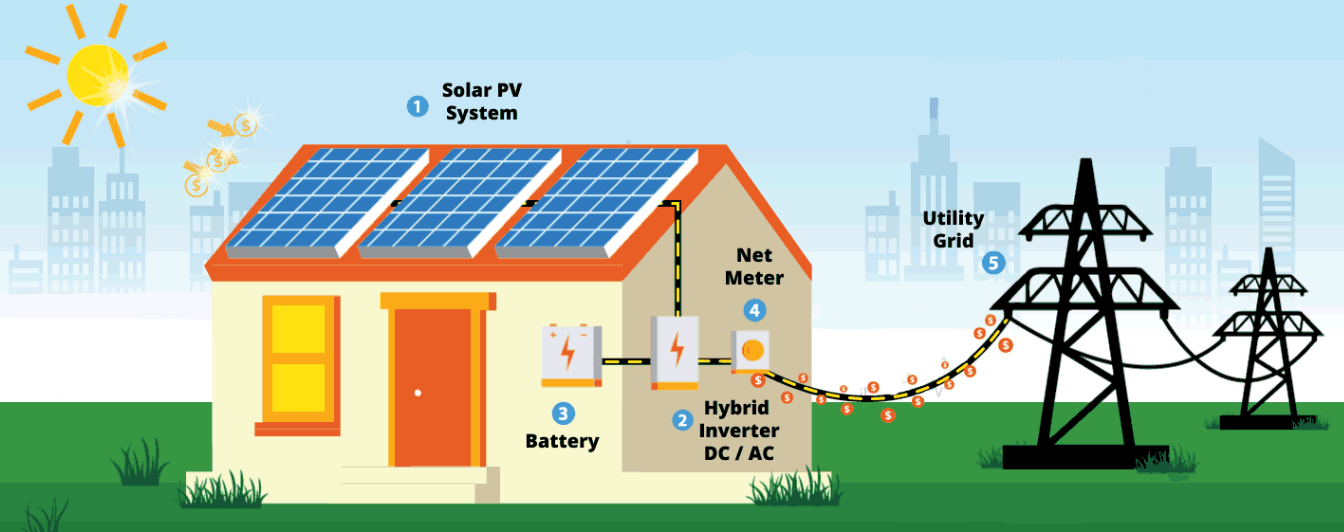
Net metering is a billing mechanism that allows consumers who generate their own electricity, such as through solar panels, to receive credit for the excess electricity they feed back into the grid. Traditionally, net metering applies to individual consumers with their own solar installations.
How Does Virtual Net Metering Work?
Virtual net metering extends the concept of net metering to multiple consumers who may not have access to solar panels or suitable rooftops for installation. In this system, a single solar energy system, often located in a centralized location, generates electricity that is distributed among multiple consumers. Each consumer receives credits on their utility bills for their share of the electricity generated.
Benefits of Solar Panel Virtual Net Metering
Cost Savings
One of the primary benefits of virtual net metering is its potential for cost savings. By allowing multiple consumers to share the benefits of a single solar installation, virtual net metering reduces the upfront costs associated with purchasing and installing individual solar panels. Additionally, consumers can lower their electricity bills by offsetting their consumption with credits from the shared solar system.
Environmental Impact
Virtual net metering also has significant environmental benefits. By promoting the use of renewable energy sources like solar power, virtual net metering reduces reliance on fossil fuels and helps mitigate climate change. Furthermore, by enabling more consumers to participate in solar energy generation, virtual net metering contributes to the widespread adoption of clean energy technologies.
Community Engagement
Another advantage of virtual net metering is its potential to foster community engagement. By allowing consumers to collectively invest in and benefit from solar energy projects, virtual net metering promotes a sense of ownership and collaboration within communities. This can lead to increased awareness of environmental issues and encourage further investment in renewable energy initiatives.
Implementation of Virtual Net Metering Programs
Policy and Regulation
The implementation of virtual net metering programs is heavily influenced by policy and regulation at the local, state, and national levels. Governments play a crucial role in creating favorable conditions for virtual net metering through incentives, rebates, and supportive regulatory frameworks. Clear guidelines and standards are essential to ensure the fair and effective operation of virtual net metering systems.
Technical Considerations
From a technical standpoint, implementing virtual net metering requires careful planning and coordination. Factors such as system design, metering infrastructure, and grid integration must be carefully considered to ensure reliable and efficient operation. Collaboration between utilities, solar developers, and regulatory authorities is key to overcoming technical challenges and maximizing the benefits of virtual net metering.
Challenges and Limitations
Regulatory Hurdles
Despite its potential benefits, virtual net metering faces several challenges, particularly in terms of regulatory hurdles. In some jurisdictions, outdated regulations and policies may hinder the widespread adoption of virtual net metering programs. Addressing these regulatory barriers requires proactive engagement from policymakers and stakeholders to enact reforms that support the growth of virtual net metering.
Technical Constraints
Technical constraints also pose challenges to the implementation of virtual net metering. Issues such as grid capacity, voltage regulation,
What is virtual net metering?
- Virtual net metering is a billing arrangement that enables multiple energy consumers to share the benefits of a single solar energy system. Unlike traditional net metering, where each consumer must have their own solar installation, virtual net metering allows consumers to receive credits for electricity generated by a shared solar system, even if it is not located on their property.
How does virtual net metering differ from traditional net metering?
- The primary difference between virtual net metering and traditional net metering lies in the ownership and location of the solar energy system. With traditional net metering, consumers must have their own solar panels installed on their property to receive credits for excess electricity generation. In contrast, virtual net metering allows consumers to benefit from a shared solar installation, regardless of its location.
What are the benefits of virtual net metering for consumers?
- Virtual net metering offers several benefits for consumers, including:
- Cost savings: By sharing the costs of a single solar energy system, consumers can enjoy lower electricity bills and reduced upfront expenses compared to individual installations.
- Environmental impact: Virtual net metering promotes the use of clean, renewable energy sources like solar power, which helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions and combat climate change.
- Community engagement: Virtual net metering encourages collaboration among community members, fostering a sense of ownership and shared responsibility for sustainable energy initiatives.
What are some challenges associated with implementing virtual net metering programs?
- Implementing virtual net metering programs can be challenging due to various factors, including:
- Regulatory hurdles: Outdated regulations and policies may hinder the adoption of virtual net metering, requiring policymakers to enact reforms to support its implementation.
- Technical constraints: Grid capacity, voltage regulation, and interconnection standards must be addressed to ensure the seamless integration of solar energy systems into existing infrastructure.
- Economic factors: The upfront costs of solar installations and infrastructure can limit access to virtual net metering programs for some consumers, necessitating financing options and incentives to make them more accessible.
How can communities and policymakers support the expansion of virtual net metering?
Communities and policymakers can support the expansion of virtual net metering by:
- Advocating for supportive policies and regulations that facilitate the implementation of virtual net metering programs.
- Investing in grid modernization and infrastructure upgrades to accommodate the integration of solar energy systems.
- Providing financial incentives, rebates, and financing options to make virtual net metering more accessible and affordable for consumers.